The EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) is a significant legislative measure aimed at combating deforestation and forest degradation linked to the European Union's consumption of certain commodities. This document provides an overview of the EUDR, its objectives, key provisions, and implications for businesses and stakeholders involved in the supply chains of affected products. The regulation is part of the EU's broader commitment to sustainability and environmental protection, reflecting the urgent need to address climate change and biodiversity loss.

Introduction
The EUDR was introduced to ensure that products sold in the EU do not contribute to deforestation or forest degradation, either directly or indirectly. This regulation targets specific commodities that are known to drive deforestation, such as palm oil, cocoa, coffee, and soy, among others. By implementing strict due diligence requirements, the EU aims to promote sustainable sourcing practices and protect global forests.

Objectives of the EUDR
Prevent Deforestation: The primary goal is to eliminate the EU's contribution to global deforestation and forest degradation.
Promote Sustainable Supply Chains: Encourage businesses to adopt sustainable practices in sourcing commodities.
Enhance Transparency: Improve traceability of products to ensure they are not linked to deforestation.
Support Global Efforts: Align with international agreements and commitments to combat climate change and protect biodiversity.

Key Provisions
Scope of the Regulation
The EUDR applies to a range of commodities and products, including but not limited to:
Palm oil
Cocoa
Coffee
Soy
Timber
Rubber

Due Diligence Requirements
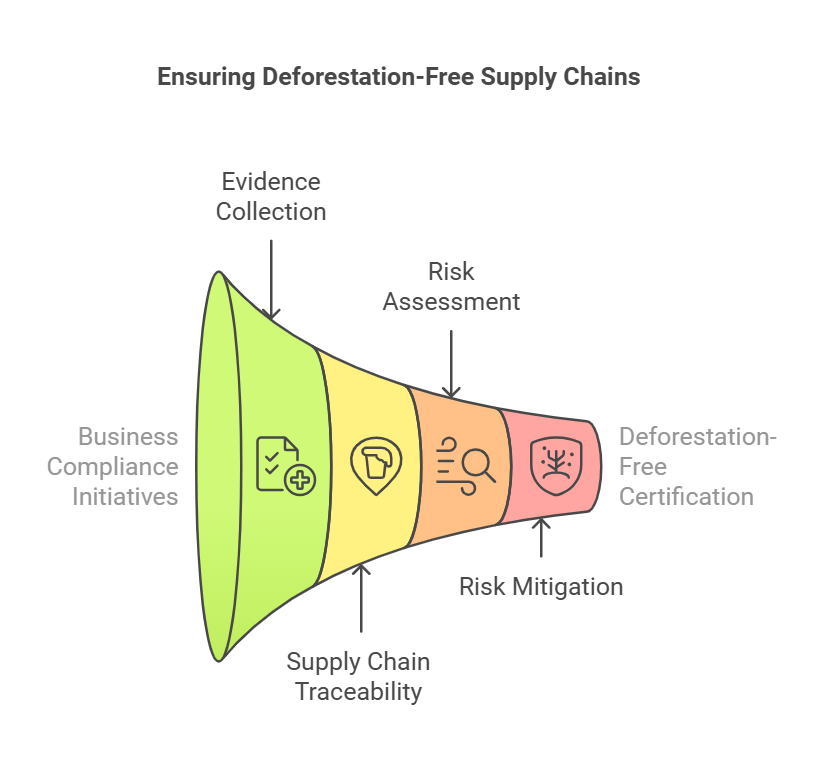
Businesses are required to conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that their products are not linked to deforestation. This includes:
Providing evidence of compliance with the regulation.
Demonstrating traceability of the supply chain.
Assessing and mitigating risks associated with deforestation.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
The regulation establishes penalties for companies that fail to comply with the due diligence requirements. These may include fines, restrictions on market access, and reputational damage.

Implications for Businesses
The EUDR presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses operating within the EU market. Companies will need to invest in sustainable sourcing practices and enhance their supply chain transparency. However, those that adapt to these requirements may benefit from increased consumer trust and a competitive advantage in the growing market for sustainable products.

Conclusion
The EU Deforestation Regulation represents a crucial step towards achieving sustainability and protecting the world's forests. By holding businesses accountable for their sourcing practices, the EUDR aims to create a more sustainable future and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Stakeholders across the supply chain must collaborate to ensure compliance and promote responsible consumption within the EU.

Comments